tensorflow serving模型加载高延迟问题排查
阅读次数:
笔者预设读者对tensorflow serving(下文简称tf)有一定了解基础,因此在一些和本文不太相关的tf相关知识不会做过多描述。本文介绍的从源码层面分析在生产环境碰到tf模型加载高延迟的一次问题排查过程。
问题背景
tf在生产环境部署投入使用一段时间后,发现每次更新tf模型加载配置文件model.config到tf加载完模型时间间隔偶尔会变得很长,而且这个时间变长的频率越来越高。更新model.config到tf加载模型完成正常的时间是10s左右,一般都会在20s内加载完成模型。但现在这个时间可能会达到分钟级别。
注:tf部署在k8s,云厂商为华为云,模型存储在华为云对象存储obs上,tf通过挂载obs访问模型路径。
我们抓取了日志,日志显示09:59:19修改了tf模型配置文件,tf 09:59:58开始加载模型,10:00:01完成模型加载。
tf模型加载流程
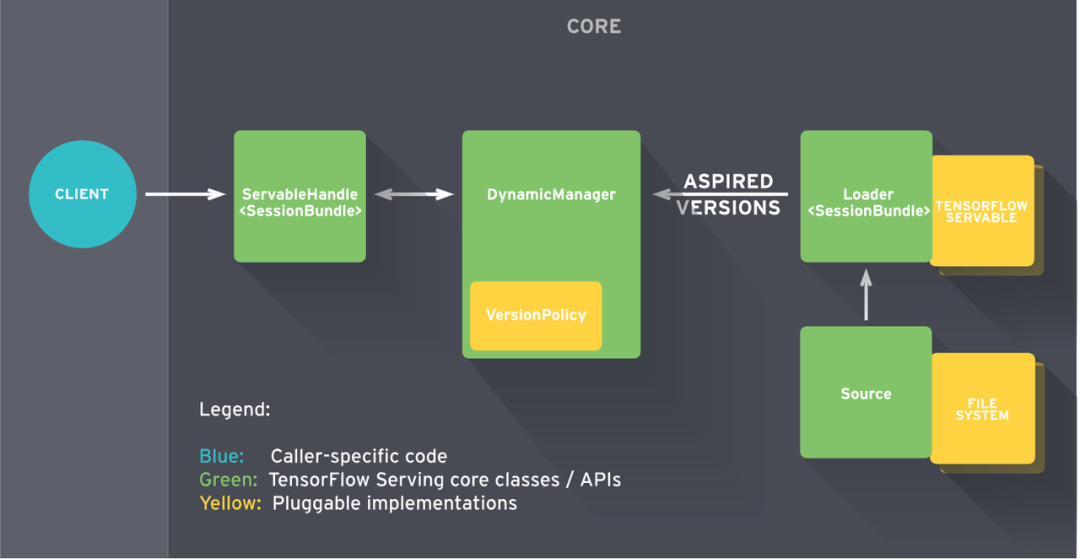
Source是tf定义的对未加载模型对象的抽象,目前实现了两种Source,一种是StaticStoragePathSource,一种是FileSystemStoragePathSource。 前者是简单的静态的模型文件存储系统,仅仅在启动时触发模型的加载,没有其他动作。后者是动态的Source,能监测存储系统的变化并发出通知。
tf实现Source时将模块职责划分的很清晰,Source的职责就是监测变化,如何处理则由Source的用户决定,所以Source有一个接口SetAspiredVersionsCallback, 可以设置回调函数用于通知AspiredVersion的变化。Source在变化的时候就会调用设置的回调函数。
作为Source的对等对象,系统也定义了Target,有接口GetAspiredVersionsCallback,用于获取处理AspiredVersions的回调接口,然后我们就可以将Target和Source连起来了。
template <typename T> void ConnectSourceToTarget(Source<T>* source, Target<T>* target) {
source->SetAspiredVersionsCallback(target->GetAspiredVersionsCallback());
}
Source和ServerCore的关系是这样的:
Source --> Router --> Adapter --> AspiredVersionManager
上述连接关系里,Router和Adapter既是Source又是Target,AspiredVersionManager是Target。但是Router没有实现Source接口,而是要求在创建Router对象时直接将Adapter作为参数,这样实现主要目的是创建一对多的关系。
系统根据所支持平台的个数(tensorflow算是一种平台)创建Adapter,一种平台对应一个Adapter,负责创建模型加载器Loader。对于tensorflow平台,对应的adapter是SavedModelBundleSourceAdapter。
Router负责根据模型名称查找对应的平台(model.config里面有指定平台名称),从而定位到对应的Adapter。
这些连接关系是在系统启动, 或者更新model.config的时候建立的。
默认配置下,FileSystemStoragePathSource为Source的实例,SavedModelBundle-SourceAdapter为Adapter的实例,DynamicSourceRouter为Router的实例:
- FileSystemStoragePathSource有自己单独的工作线程, 周期查询文件系统, 发现每个模型的版本, 根据指定的servable_version_policy(model_config), 创建ServableData(模型名, 版本号, 路径), 传给Router
- Router根据路由找到对应的adapter, 传给Adataper
- Adapter将ServableData(模型名, 版本号, 路径)转换成ServableData(模型名, 版本, Loader), 传给AspiredVersionManager
- AspiredVersionManager将这些信息存到pending_aspired_versions_requests_, 等待另外一个工作线程(AspiredVersionsManager_ManageState_Thread)处理。
具体请参考该文章:《Tensorflow Serving的原理和代码实现》
小结:有一个工作线程,周期查询model.config模型配置文件,并将配置的模型转换成ServableData,并转换传给AspiredVersionManager。且AspiredVersionManager会起一个工作线程处理ServableData对应的模型。
排查过程
查看日志
周期性检查一次model.config文件耗时偶尔会耗时很高,有时十几秒,有时一分多钟。且阻塞在Finished adding/updating models前的步骤上。
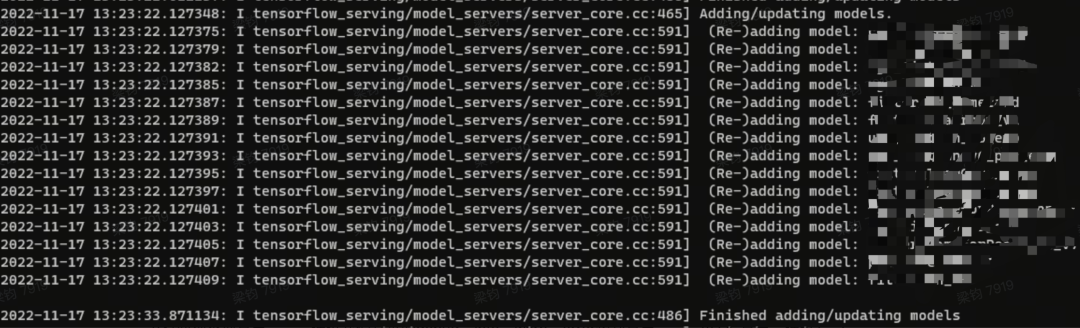
开启TF的VLOG日志
tf有两种类型日志,一是通过我们常见的debug,info,warn,error级别日志,一是VLOG日志,通过1,2,3,4区分日志级别。
## tf启动增加如下参数开启VLOG(1)级别参数
--TF_CPP_MAX_VLOG_LEVEL=1
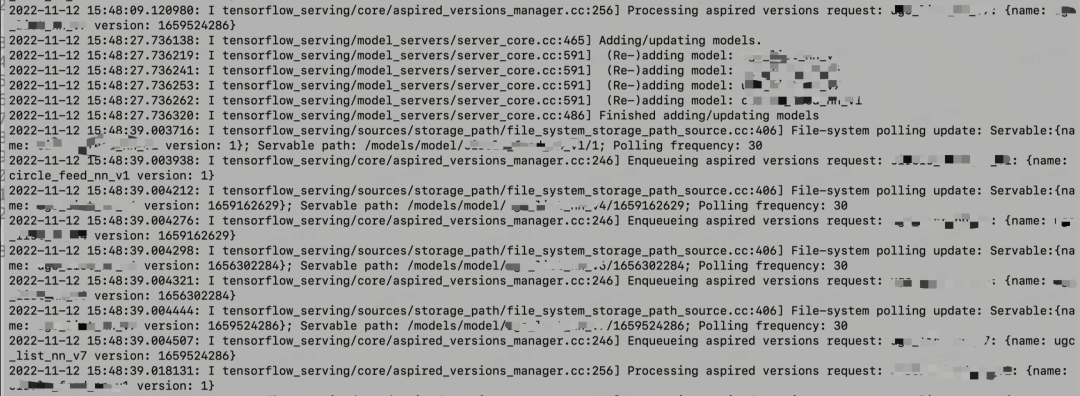
通过日志可知,tf除了周期性检查model_config文件,还会周期性检查已加载的模型(也就是前面所讲AspiredVersionManager周期性检查ServableData模型的工作线程)。此时开始怀疑是否这两个线程是否存在锁的竞争,导致周期检查model_config的线程长期处于饥饿状态。
周期性检查已加载模型任务线程代码分析
AspiredVersionManager会起一个工作线程处理ServableData,对应的模型代码分析:
// 线程任务函数
const auto thread_fn = [this](void) {
Status status = this->PollFileSystemAndInvokeCallback();
if (!status.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "FileSystemStoragePathSource encountered a "
"filesystem access error: "
<< status.error_message();
}
};
// Start a thread to poll the filesystem periodically and call the callback.
PeriodicFunction::Options pf_options; // 起定时器左右
pf_options.thread_name_prefix =
"FileSystemStoragePathSource_filesystem_polling_thread";
// 周期性执行thread_fn
fs_polling_thread_.reset(new FileSystemStoragePathSource::ThreadType(
absl::in_place_type_t<PeriodicFunction>(), thread_fn,
config_.file_system_poll_wait_seconds() * 1000000, pf_options));
}
Status FileSystemStoragePathSource::PollFileSystemAndInvokeCallback() {
mutex_lock l(mu_); // 获取mu_互斥锁
std::map<string, std::vector<ServableData<StoragePath>>>
versions_by_servable_name;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
PollFileSystemForConfig(config_, &versions_by_servable_name));
for (const auto& entry : versions_by_servable_name) {
const string& servable = entry.first;
const std::vector<ServableData<StoragePath>>& versions = entry.second;
if (versions.empty() && config_.servable_versions_always_present()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Refusing to unload all versions for Servable: "
<< servable;
continue;
}
for (const ServableData<StoragePath>& version : versions) {
if (version.status().ok()) {
VLOG(1) << "File-system polling update: Servable:" << version.id()
<< "; Servable path: " << version.DataOrDie()
<< "; Polling frequency: "
<< config_.file_system_poll_wait_seconds();
}
}
CallAspiredVersionsCallback(servable, versions);
}
return Status::OK();
}
tf会创建PeriodicFunction对象来周期性调用PollFileSystemAndInvokeCallback,周期时间间隔取决于配置file_system_poll_wait_seconds(不设置tf启动默认赋值1s),而在PollFileSystemAndInvokeCallback需要获取锁mu_。
而tf如何周期性执行任务可以看PeriodicFunction相关代码:
void PeriodicFunction::RunLoop(const int64_t start) {
{
if (options_.startup_delay_micros > 0) {
const int64_t deadline = start + options_.startup_delay_micros;
options_.env->SleepForMicroseconds(deadline - start);
}
while (!stop_thread_.HasBeenNotified()) {
VLOG(3) << "Running function.";
const int64_t begin = options_.env->NowMicros();
function_();
// Take the max() here to guard against time going backwards which
// sometimes happens in multiproc machines.
const int64_t end =
std::max(static_cast<int64_t>(options_.env->NowMicros()), begin);
// The deadline is relative to when the last function started.
const int64_t deadline = begin + interval_micros_;
// We want to sleep until 'deadline'.
if (deadline > end) {
if (end > begin) {
VLOG(3) << "Reducing interval_micros from " << interval_micros_
<< " to " << (deadline - end);
}
options_.env->SleepForMicroseconds(deadline - end);
} else {
VLOG(3) << "Function took longer than interval_micros, so not sleeping";
}
}
}
}
进入while循环里面:
- 获取当前时间赋值begin。
- 执行任务函数:扫描obs获取当前加载模型路径下的目录,校验加载模型的正确性
- 取当前时间赋值给end。
- 计算deadline ,deadline = begin + interval_micros_,interval_micros_即是上文讲的file_system_poll_wait_seconds。
- 如果deadline > end,进入睡眠,否则,循环回到第一步。
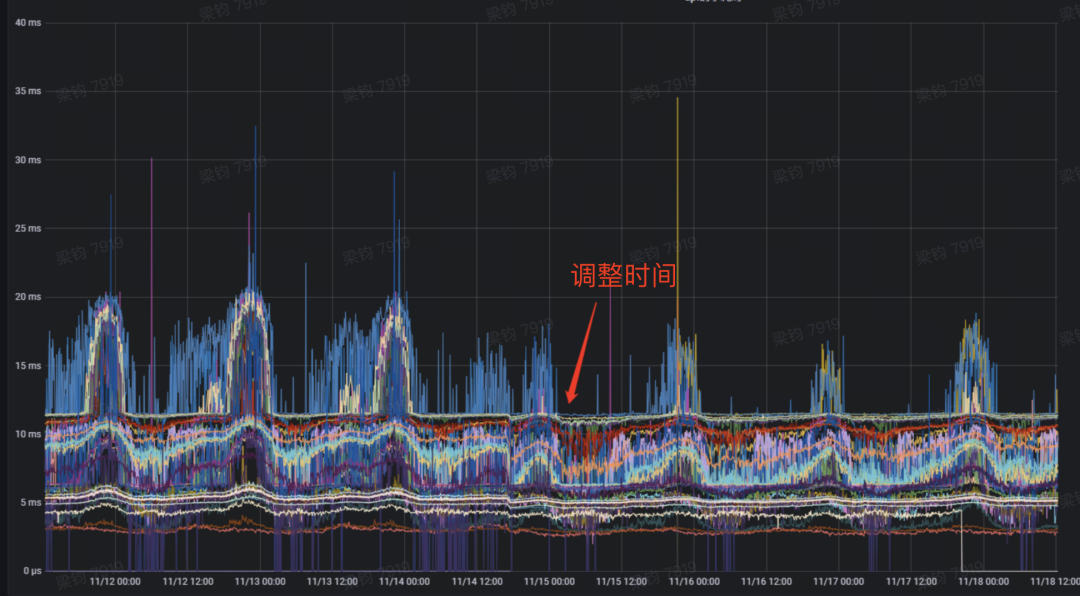
总结:周期性检查model.config的任务线程和周期性检查已加载模型的任务线程竞争同一互斥锁mu_,又由于file_system_poll_wait_seconds没有设置,默认1s执行一次任务,随着加载中的模型较多,且读取一次obs耗时较高,导致不断循环竞争互斥锁mu_,检查model_config任务长时间处于饥饿状态,任务阻塞,以至于模型加载延迟高。后调整file_system_poll_wait_seconds解决了该问题。 另:k8s虽然可以通过挂载对象存储至pod上,可以像访问本地存储访问对象存储,但本质访问对象存储是通过网络调用拉取远程数据,所以这个网络调用耗时不能忽视,调用耗时过高会影响周期性检查已加载模型的任务执行,从而给tf带来一定的性能影响。
当调整file_system_poll_wait_seconds之后,tf的模型推理预测P99毛刺有一定优化效果: